The Complete Guide to Creative Innovation
Frameworks, Culture, and Technology for Growth
In a world of accelerating change, "innovation" is more than a buzzword—it's the primary engine of survival and growth. But true innovation isn't born from random sparks of genius; it's a disciplined, repeatable process. This is the domain of creative innovation: a systematic approach that blends human-centered design, strategic problem-solving, and the amplifying power of technology to generate novel solutions that create real value.
While traditional innovation often focuses on incremental improvements to existing products, creative innovation seeks to reframe the problem itself. It asks not just "How can we build this better?" but "What should we be building in the first place?" This guide is a comprehensive deep dive into the frameworks, cultural shifts, and technological catalysts that empower organizations to move beyond optimization and into the realm of true transformation.
The Philosophy: Balancing Divergent and Convergent Thinking
At its core, creative innovation is a structured process of balancing two distinct modes of thinking: divergence and convergence.
- Divergent Thinking: This is the process of idea generation. It's about exploring possibilities, brainstorming without judgment, and creating a wide range of potential solutions to a problem. The goal is quantity over quality, casting as wide a net as possible.
- Convergent Thinking: This is the process of idea evaluation and selection. It involves analyzing, critiquing, and narrowing down the generated ideas to identify the most promising, feasible, and viable options to move forward.
The entire creative innovation process is a rhythmic dance between these two modes. You diverge to create choices, then converge to make choices. This structured approach prevents teams from either getting stuck in endless brainstorming or prematurely committing to the first plausible idea.
Frameworks for Creative Problem-Solving
To turn the philosophy of creative innovation into practice, organizations rely on structured frameworks. These models provide a roadmap for navigating ambiguity, challenging assumptions, and systematically moving from problem to solution.
Case Studies in Creativity
Creative innovation isn't just a theory. Here are real-world examples of how forward-thinking companies redefined their industries by challenging the status quo.
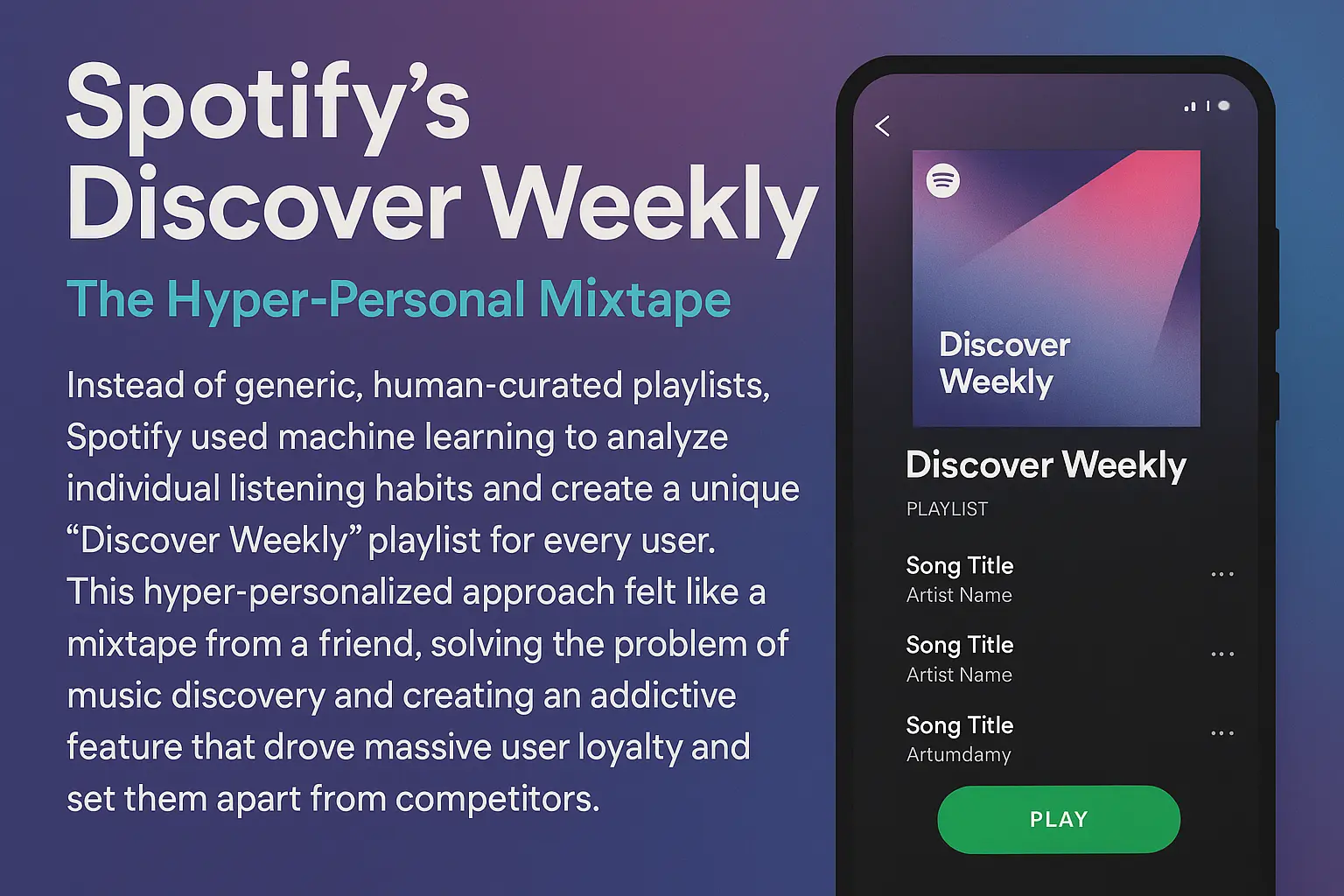
Spotify's Discover Weekly
The Hyper-Personal Mixtape
Instead of generic, human-curated playlists, Spotify used machine learning to analyze individual listening habits and create a unique "Discover Weekly" playlist for every user. This hyper-personalized approach felt like a mixtape from a friend, solving the problem of music discovery and creating an addictive feature that drove massive user loyalty and set them apart from competitors.
Patagonia's "Don't Buy This Jacket"
The Anti-Advertisement
On Black Friday, the biggest shopping day of the year, Patagonia ran a full-page ad in The New York Times with the headline "Don't Buy This Jacket." This shocking, counter-intuitive campaign promoted sustainability and repair over mindless consumption, generating immense brand trust and proving that a strong mission can be the most powerful marketing tool.

Airbnb Experiences
Selling Experiences, Not Just Stays
To evolve beyond just accommodation, Airbnb launched "Experiences"—curated activities designed and hosted by local experts. This brilliant pivot transformed the company from a simple booking platform into an end-to-end travel service, capturing more customer spending and fulfilling its core mission to help people "Belong Anywhere."

Design Thinking: The Human-Centered Core
Design Thinking is arguably the most influential framework for creative innovation. It is a human-centered, solutions-based process that integrates the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success. Its power lies in its relentless focus on empathy—understanding the end-user's unspoken needs, pain points, and motivations before a single solution is sketched.
The typical Design Thinking process follows five iterative phases:
- Empathize: Conduct thorough research to gain a deep understanding of your users' experiences and challenges. This involves observation, interviews, and immersing yourself in their world.
- Define: Synthesize your research findings to articulate a clear, actionable problem statement, often framed as a "How Might We...?" question. This reframes the problem from an obstacle into an opportunity.
- Ideate: Brainstorm a wide range of potential solutions to the problem statement. This is a purely divergent phase where judgment is deferred, and wild ideas are encouraged.
- Prototype: Create low-fidelity, inexpensive, and testable versions of the most promising solutions. A prototype can be anything from a paper sketch or a role-playing scenario to a simple clickable model.
- Test: Share your prototypes with real users to gather feedback. The goal is to learn what works, what doesn't, and refine your solution based on real-world interaction. This phase often leads back to earlier stages, making the process highly iterative.
First Principles Thinking: Deconstructing the Problem
Popularized by innovators like Elon Musk, First Principles Thinking is a method of breaking down complex problems into their most basic, fundamental truths and reasoning up from there. Instead of relying on analogies or past conventions ("the way it's always been done"), this framework forces you to question every assumption.
The process involves:
- Identify the Problem: Clearly state the challenge you are trying to solve.
- Deconstruct Assumptions: List all the current beliefs and assumptions associated with the problem. For example, if the problem is "building a cheaper battery," an assumption might be "batteries will always be expensive because the raw materials are expensive."
- Isolate the First Principles: Challenge each assumption until you are left with only fundamental, undeniable truths. In the battery example, a first principle might be: "What are the base materials a battery is made of, and what is their spot market value?"
- Reconstruct from the Ground Up: Using these fundamental truths as your building blocks, start to formulate a new solution, free from the constraints of prior conventions.
This framework is incredibly powerful for tackling entrenched industry problems and achieving breakthrough innovations rather than incremental improvements.
Innovation by the Numbers
Creativity is more than an abstract concept; it's a measurable driver of global success. These industry-wide metrics reveal the tangible impact of strategic innovation on business growth, market leadership, and financial valuation.
79%
Top Priority
(Percentage of companies that rank innovation as a top-three priority)
3.5x
Higher Growth
(Creative companies are 3.5 times more likely to achieve significant revenue growth)
1.2K
Unicorns Globally
(Number of private companies valued at over $1 billion, fueled by innovation)
From Structure to Story: The Role of Creative Innovation
This diagram illustrates the essential technical framework—the "machine"—of modern content marketing. But a framework alone doesn't build a community. Creative innovation is the catalyst that breathes life into this structure, transforming technical processes into compelling human stories. It’s the art of using these tools not just for efficiency, but to create truly valuable content and foster genuine dialogue, turning a one-way message into a loyal and engaged audience.
Frameworks for Breakthrough Thinking
Creativity thrives on structure. We leverage proven frameworks to move beyond guesswork and systematically navigate the path to innovation. These methodologies provide a repeatable process for identifying a problem's root cause, discovering inventive solutions, and building the cultural foundation required for success.
The 5 Whys Method: Uncovering the Root Cause
Often, the problem we see is merely a symptom of a deeper, underlying issue. The 5 Whys method is a simple but powerful interrogative technique used to explore the cause-and-effect relationships behind a particular problem. By repeatedly asking "Why?" (five is a rule of thumb), you can peel back the layers of symptoms and identify the root cause.
TRIZ (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving)
TRIZ is a systematic framework that posits that most inventive problems have already been solved somewhere before, in some other industry or field.
Developed by analyzing millions of patents, TRIZ identifies universal principles of invention.

Building a Culture of Creative Innovation
Frameworks are essential, but they are only effective within an organizational culture that actively supports and nurtures creativity.
Without the right environment, even the best processes will fail.

The Innovation Playbook
Breakthroughs don't happen by accident; they are nurtured in a carefully designed environment. This playbook outlines the essential strategies for fostering true innovation, from cultivating the human elements of psychological safety and collaborative leadership to leveraging powerful technological catalysts like AI and XR.
Psychological Safety: The Freedom to Fail
Innovation requires risk-taking. Team members must feel safe enough to propose unconventional ideas, challenge the status quo, and, most importantly, fail without fear of punishment or humiliation. A psychologically safe environment is the bedrock of a creative culture. Leaders can foster this by:
- Modeling Vulnerability: Admitting their own mistakes and uncertainties.
- Framing Work as a Learning Process: Emphasizing experimentation and iteration over immediate perfection.
- Promoting Curiosity: Actively soliciting questions and rewarding inquiry.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Breaking Down Silos
The most powerful innovations often occur at the intersection of different disciplines. A culture of creative innovation actively breaks down departmental silos, encouraging collaboration between engineering, marketing, design, sales, and customer support.
This diversity of perspectives is crucial for seeing a problem from all angles and developing holistic solutions. Higher-growth brands are significantly more likely to encourage this kind of cross-functional collaboration.
Leadership and Empowerment
Leadership plays a critical role in either stifling or enabling innovation. An innovative culture requires leaders who:
- Provide a Clear Vision: Set a compelling direction but allow teams the autonomy to figure out how to get there.
- Champion Good Ideas: Protect nascent ideas from premature criticism and provide the resources needed for experimentation.
- Encourage "Cocreation": Recognize that great ideas can come from anywhere—not just from within the organization, but from external partners, suppliers, and even customers.
The Role of Technology as a Catalyst
Technology is a great amplifier of creative innovation. It provides the tools to execute creative ideas at scale, analyze problems with unprecedented depth, and visualize solutions in entirely new ways.
Generative AI: The Creative Co-Pilot
Generative AI is transforming the ideation process. By generating hundreds of design variations, copy options, or even code snippets in seconds, AI acts as a tireless brainstorming partner. This doesn't replace human creativity; it augments it. It handles the divergent thinking phase at a massive scale, allowing human innovators to focus on the convergent tasks of curation, refinement, and strategic selection.
Extended Reality (XR): Prototyping in the Virtual World
Virtual and Augmented Reality (XR) are revolutionizing the prototyping and testing phases of innovation. Instead of building expensive physical models, designers and engineers can create immersive, interactive digital twins of products, buildings, or user experiences. This allows for rapid, low-cost iteration and enables stakeholders and customers to experience a solution in a realistic context long before it's built, leading to more insightful feedback and better final products.
Data Analytics & Visualization: Uncovering Hidden Needs
Advanced data analytics allows organizations to move beyond intuition and understand customer behavior with empirical precision. By analyzing vast datasets, companies can identify unmet needs and friction points that customers themselves may not even be able to articulate. Creative data visualization then transforms this raw data into compelling, human-understandable stories, building empathy and aligning the entire organization around the true nature of the customer's problem.
Creative innovation is not a mystical art but a strategic capability. By combining human-centered frameworks, a supportive culture, and the amplifying power of technology, any organization can build a sustainable engine for growth and create a future that is not just predicted, but designed.
Unlocking Growth: How Creative Technology is Revolutionizing Business and Work
Explore the impact of AI, immersive experiences, and decentralized tech on how we generate revenue, run our businesses, and build the workforce of tomorrow.

Let's Build Your Breakthrough
You've seen the frameworks and the case studies. Now, let's apply them. Whether you're facing a complex challenge or launching a new venture, our team is ready to help you architect the path from idea to impact.